Data Snapshot Solution - Power BI & Power Automate
Introduction
In today's data-driven world, organizations need efficient ways to capture and maintain historical data snapshots. This guide demonstrates how to build an automated solution using Microsoft Power Platform that seamlessly handles data capture, transformation, and storage.
Overview of the Solution
Our automated snapshot solution combines three powerful Microsoft tools:
Power Automate for workflow orchestration
Power BI for data transformation and staging
Office Scripts for Excel automation
This integration creates a robust, scalable system for maintaining historical data records.
Setting Up the Data Pipeline
1. Power BI as the Data Foundation
Power BI serves as our intelligent staging area, offering:
Connectivity to multiple data sources (Dataverse, SQL, etc.)
Robust data transformation through Power Query
Scheduled automatic refreshes via the Power BI Web Service
Consistent data structure maintenance
Best Practice: Design your Power BI data model with incremental refresh for optimal performance with large datasets.
2. Excel Automation with Office Scripts
The Office Script handles data processing and formatting:
async function main(workbook: ExcelScript.Workbook, jsonString: string): Promise<{ status: string, message: string }> {
try {
// Parse JSON data
let jsonData: Record<string, string | number | boolean>[];
try {
jsonData = JSON.parse(jsonString);
} catch (error: unknown) {
return { status: "error", message: "Invalid JSON format. Please provide a valid JSON string." };
}
// Convert JSON to 2D array for Excel
const headers = Object.keys(jsonData[0]);
const rows = jsonData.map(obj => headers.map(key =>
typeof obj[key] === "string" ? `'${obj[key]}` : obj[key]
));
const result = [headers, ...rows];
// Create new worksheet
const newSheetName = "ExportedData";
let newWorksheet = workbook.getWorksheet(newSheetName);
if (newWorksheet) {
newWorksheet.delete();
}
newWorksheet = workbook.addWorksheet(newSheetName);
// Process data in batches of 1000 rows
const rowCount = result.length;
const colCount = result[0].length;
const batchSize = 1000;
for (let startRow = 0; startRow < rowCount; startRow += batchSize) {
const endRow = Math.min(startRow + batchSize, rowCount);
const batchData = result.slice(startRow, endRow);
const destinationRange = newWorksheet.getRangeByIndexes(startRow, 0, batchData.length, colCount);
destinationRange.setValues(batchData);
}
// Format as table
const fullRange = newWorksheet.getRangeByIndexes(0, 0, rowCount, colCount);
const newTable = newWorksheet.addTable(fullRange, true);
newTable.setName("ExportedTable");
return { status: "success", message: `Successfully inserted ${rowCount} rows into '${newSheetName}'.` };
} catch (error: unknown) {
return { status: "error", message: `An unexpected error occurred: ${(error as Error).message}` };
}
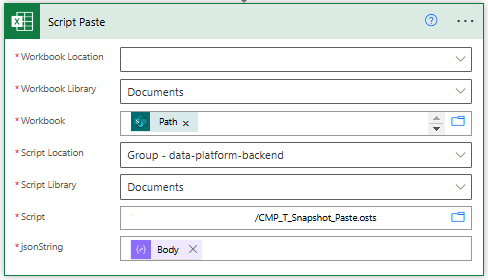
}Power Automate Run Office Script
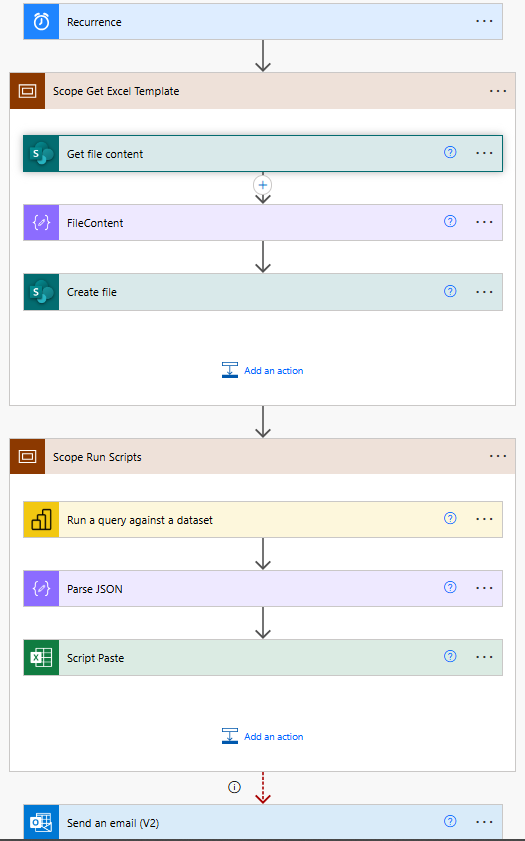
3. Power Automate Workflow Configuration
The workflow automation consists of these key steps:
File Template Retrieval
Action: "Get file content"
Site Address: Your SharePoint site (e.g., https://[your-org].sharepoint.com/sites/data-platform-backend)
File Identifier: Path to your template (e.g., /Shared Documents/snapshots-timeline/Template.xlsx)
File Content Processing
Action: "FileContent"
Input: Body from the previous "Get file content" step
This step prepares the template content for the new file creation
New File Creation
Action: "Create file"
Site Address: Same SharePoint site as template
Folder Path: Destination folder (e.g., /Shared Documents/snapshots-timeline/Snapshots)
File Name: Dynamic naming (e.g., "CMP_T_{formatDate}.xlsx")
File Content: Output from the FileContent step
Data Population
Executes Power BI query against the dataset using “Evaluate YourQueryName”
Processes the returned data
Uses Office Scripts to format and structure the data
Completion Actions
Sends email notifications
Updates status logs
Handles any error conditions
Power Automate for workflow orchestration
Conclusion
This Microsoft Power Platform solution provides a robust framework for automated data snapshot management. By leveraging the strengths of each component, organizations can maintain reliable historical data records with minimal manual intervention.